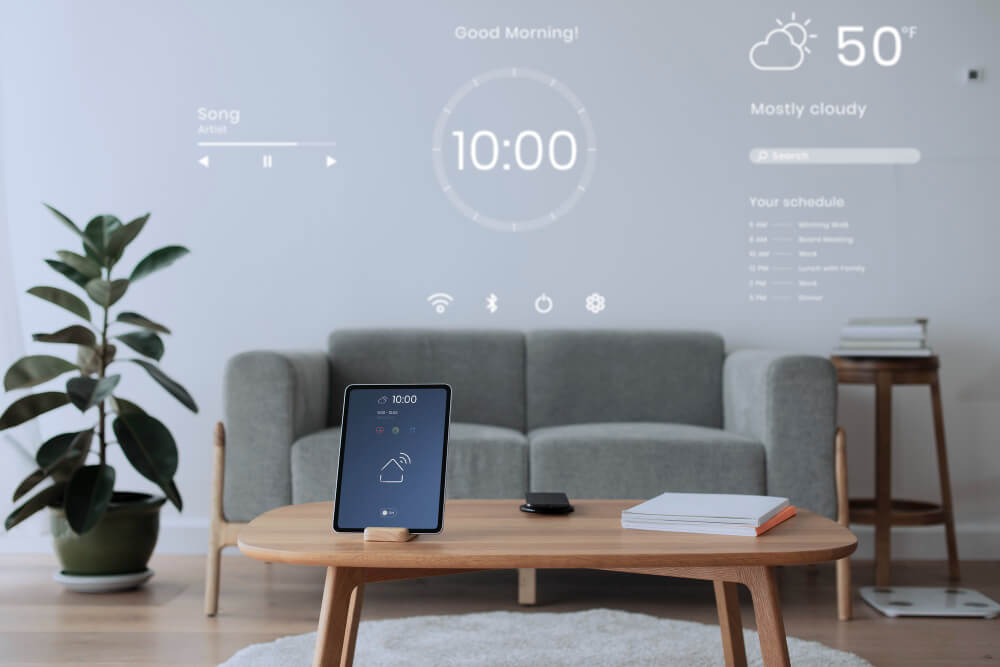
Smart home devices have rapidly transformed from a futuristic concept to an integral part of modern living. With the promise of convenience, efficiency, and connectivity, these devices have revolutionized the way we interact with our homes. In this blog post, we will explore the evolution of smart home technology, tracing its origins, examining key advancements, and envisioning its future implications. From science fiction to everyday reality, the journey of smart home devices is a fascinating one, filled with innovation and endless possibilities.
Early Beginnings
The roots of smart home technology can be traced back to the early experiments and concepts that laid the foundation for what we know today. In the not-so-distant past, visionaries and inventors began exploring ways to automate and control various aspects of home life. From rudimentary systems to more sophisticated prototypes, these early endeavors set the stage for the evolution of smart home devices.
Origins of smart home technology
The origins of smart home technology can be traced back to the convergence of various fields, including electronics, computing, and telecommunications. While the concept of automating household tasks and controlling home appliances remotely dates back several decades, the term “smart home” gained prominence in the late 20th century as advancements in technology began to make interconnected, automated homes a reality.
The rise of personal computers in the 1990s further accelerated the development of smart home technology. With computers becoming more powerful and affordable, developers began creating software and hardware solutions that enabled users to monitor and control their homes remotely. This era saw the emergence of early home automation systems that allowed users to set schedules, monitor security cameras, and adjust thermostat settings from their desktop computers.
In the 21st century, the proliferation of wireless communication technologies, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, fueled the expansion of smart home devices. These wireless standards enabled seamless connectivity between devices, paving the way for the development of interconnected smart home ecosystems. Coupled with advancements in sensors, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing, smart home technology continued to evolve, offering users unprecedented levels of convenience, comfort, and security.
Today, smart home technology encompasses a wide range of devices and systems, including smart thermostats, lighting controls, security cameras, voice assistants, and more. As technology continues to advance and become more integrated into our daily lives, the possibilities for smart home innovation are endless, promising to transform the way we live, work, and interact with our homes.
Rise of Connectivity and Control
The rise of connectivity and control marks a pivotal era in the evolution of smart home devices. As technology advanced, so did the capabilities of these devices, enabling seamless communication and centralized management within the home environment.
Introduction of Wi-Fi and its impact on smart home technology
The advent of Wi-Fi technology revolutionized the landscape of smart home devices, ushering in a new era of connectivity and convenience. Wi-Fi-enabled devices offer users the ability to connect to their home network wirelessly, eliminating the need for cumbersome cables and allowing for seamless integration into existing Wi-Fi networks.
The impact of Wi-Fi on smart home technology was profound. With Wi-Fi connectivity, smart devices can be controlled remotely using smartphones, tablets, or computers, providing users with unprecedented flexibility and convenience. Whether it was adjusting the thermostat while away from home or monitoring security cameras from the office, Wi-Fi-enabled smart home devices empowered users to stay connected and in control, no matter where they were.
Furthermore, Wi-Fi technology facilitated the integration of voice control into smart home devices, enabling users to control their devices using voice commands via virtual assistants like Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant. This hands-free approach to controlling smart home devices added another layer of convenience and accessibility, making it easier than ever for users to interact with their smart home ecosystem.
In essence, the introduction of Wi-Fi technology transformed smart home devices from standalone gadgets into interconnected, intelligent systems that could be easily monitored and controlled from anywhere with an internet connection. This laid the foundation for the continued evolution of smart home technology, setting the stage for even more advanced and interconnected devices in the future.
Emergence of smart hubs and central control systems
As the number of smart home devices continued to grow, so too did the need for a centralized hub or control system to manage them effectively. Enter the emergence of smart hubs and central control systems, which serve as the nerve center of the smart home ecosystem.
Smart hubs are devices that act as a central hub for connecting and controlling various smart home devices. These hubs typically feature compatibility with multiple communication protocols, such as Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Bluetooth, allowing them to communicate with a wide range of smart devices from different manufacturers.
One of the key advantages of smart hubs is their ability to unify disparate smart home devices under a single interface, providing users with a seamless and intuitive way to control their entire smart home ecosystem. Whether it’s setting up automated routines, creating custom scenes, or monitoring device status, smart hubs offer unparalleled flexibility and customization options.
In addition to smart hubs, central control systems also emerged as a popular solution for managing smart home devices. These systems, often integrated into home automation platforms or smart speakers, provide users with a centralized interface for controlling their smart home devices using voice commands or touchscreen interfaces.
Expansion of device compatibility and interoperability
As the market for smart home devices continued to expand, so too did the need for interoperability and compatibility between different devices and manufacturers. In the early days of smart home technology, interoperability was often limited, with devices from different manufacturers using proprietary communication protocols that were incompatible with each other.
However, as the industry matured, manufacturers began adopting standardized communication protocols, such as Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Thread, to ensure interoperability between their devices and those from other manufacturers. This shift towards standardization allowed users to mix and match devices from different brands, creating custom smart home ecosystems tailored to their specific needs and preferences.
Furthermore, advancements in interoperability have paved the way for the development of integrated ecosystems and platforms that bring together multiple smart home devices under a single interface. These platforms, often referred to as smart home ecosystems or ecosystems, allow users to control and manage their smart home devices from a centralized interface, regardless of the manufacturer.
The expansion of device compatibility and interoperability has been instrumental in driving the adoption of smart home technology, making it easier than ever for users to create cohesive and interconnected smart home ecosystems. As the industry continues to evolve, interoperability will likely remain a key focus, ensuring that smart home devices remain accessible and compatible with each other, regardless of brand or manufacturer.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) has significantly enhanced the capabilities and functionalities of smart home devices, ushering in a new era of intelligence and automation. AI algorithms allow smart home devices to analyze data, learn from user behavior, and make intelligent decisions to optimize performance and enhance user experience.
Introduction of AI assistants (e.g., Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant)
The introduction of AI assistants, such as Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri, has been a game-changer in the realm of smart home technology. These virtual assistants leverage artificial intelligence algorithms to understand and respond to user commands and queries, making it easier than ever for users to interact with their smart home devices.
AI assistants are capable of performing a wide range of tasks, from controlling smart home devices to providing weather updates, setting reminders, and answering questions. Users can interact with these assistants using natural language commands, allowing for a more intuitive and hands-free experience.
For example, users can simply say, “Alexa, turn off the lights,” or “Hey Google, set the thermostat to 72 degrees,” to control their smart home devices without having to lift a finger. This hands-free approach to controlling smart home devices adds a new level of convenience and accessibility for users, especially those with mobility or accessibility needs.
Enhanced user experience and personalization
The integration of artificial intelligence has also led to enhanced user experiences and personalization within the smart home ecosystem. AI algorithms can analyze user behavior, preferences, and patterns to tailor the smart home experience to individual users’ needs and preferences.
For example, smart thermostats equipped with AI can learn users’ temperature preferences and daily routines to automatically adjust temperature settings for optimal comfort and energy efficiency. Similarly, AI-driven lighting systems can adjust brightness and color temperature based on the time of day and user preferences, creating a personalized lighting environment.
Furthermore, AI assistants can anticipate users’ needs and proactively suggest actions or reminders based on their habits and preferences. For instance, an AI assistant might remind users to water their plants or take medication at specific times of the day, based on their past behavior and routines.
Examples of AI-driven smart home devices and their functionalities
AI-powered smart thermostats
Smart thermostats equipped with AI algorithms can learn users’ temperature preferences and adjust settings automatically for optimal comfort and energy efficiency. These thermostats can also analyze external factors, such as weather forecasts and occupancy patterns, to further optimize heating and cooling schedules.
AI-driven security cameras
Security cameras equipped with AI algorithms can analyze video footage in real-time to detect and identify potential threats or suspicious activity. These cameras can send alerts to users’ smartphones or trigger other smart home devices, such as smart lights or sirens, to deter intruders.
AI-enhanced lighting systems
Lighting systems powered by AI algorithms can adjust brightness, color temperature, and even color effects based on user preferences and environmental factors. These lighting systems can create customized lighting scenes for different activities, such as reading, relaxing, or entertaining.
AI-enabled smart speakers
Smart speakers equipped with AI assistants, such as Amazon Echo or Google Nest, can control other smart home devices using voice commands. These speakers can also provide personalized recommendations, reminders, and updates based on users’ preferences and habits.
These examples illustrate the diverse range of AI-driven smart home devices available on the market today, each offering unique functionalities and capabilities to enhance the smart home experience. As AI technologies continue to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative and intelligent smart home devices emerge, further transforming the way we live, work, and interact with our homes.
Advancements in Security and Privacy
Advancements in security and privacy have been paramount in ensuring the widespread adoption and continued trust in smart home technology. As smart home devices become increasingly interconnected and integrated into our daily lives, protecting user data and safeguarding against potential security threats have become top priorities for manufacturers and developers.
Evolution of smart home security systems
The evolution of smart home security systems represents a significant advancement in protecting homes and ensuring the safety of occupants. From simple motion-sensing lights to sophisticated integrated surveillance systems, smart home security solutions have come a long way in providing comprehensive protection against intruders and emergencies.
Initially, smart home security systems primarily consisted of standalone devices such as motion sensors, door/window sensors, and security cameras. These devices would trigger alarms or notifications when they detect suspicious activity, allowing homeowners to take appropriate action.
However, as technology advanced, so did the capabilities of smart home security systems. Today’s systems are equipped with advanced features such as real-time video monitoring, two-way audio communication, and remote access via smartphone apps. Users can now monitor their homes from anywhere in the world, receive instant alerts, and even communicate with visitors or intruders remotely.
Moreover, integration with other smart home devices has further enhanced the effectiveness of smart home security systems. For example, smart locks can be integrated with security cameras and motion sensors to automatically lock doors and send alerts when unauthorized entry is detected. Similarly, smart lighting systems can be programmed to simulate occupancy and deter potential intruders when the homeowner is away.
Implementation of encryption and secure protocols
The implementation of encryption and secure protocols has been instrumental in safeguarding smart home devices and protecting user data from unauthorized access and cyberattacks. Encryption techniques such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) ensure that data transmitted between smart home devices and servers is encrypted and secure.
Additionally, the adoption of secure communication protocols such as Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Thread helps prevent unauthorized access to smart home networks and devices. These protocols incorporate built-in security features such as encryption, authentication, and authorization, making it difficult for attackers to intercept or manipulate communication between devices.
Furthermore, manufacturers regularly release firmware updates to patch known security vulnerabilities and strengthen the security of their devices. Automatic update mechanisms ensure that devices remain protected against emerging threats without requiring user intervention, helping to mitigate the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches.
Addressing privacy concerns and data protection
Addressing privacy concerns and data protection is essential to building trust and confidence in smart home technology. Manufacturers have implemented various measures to protect user privacy and ensure that personal data is handled responsibly and securely.
One of the key privacy-enhancing measures is the implementation of privacy-by-design principles, which prioritize privacy considerations throughout the design and development process of smart home devices. Manufacturers minimize the collection of sensitive data and anonymize or pseudonymize data whenever possible to protect user privacy.
Moreover, transparent privacy policies and user consent mechanisms ensure that users are aware of how their data is being collected, stored, and utilized by smart home devices and services. Users have the option to review and adjust their privacy settings, control data sharing preferences, and delete their data if desired.
Furthermore, manufacturers undergo rigorous security and privacy assessments to ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act). Regular audits and third-party security assessments help identify and address potential privacy risks and vulnerabilities, ensuring that smart home devices adhere to the highest standards of privacy and data protection.
Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Solutions
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency in the design and implementation of smart home solutions. As concerns about climate change and environmental sustainability continue to rise, smart home technology has emerged as a promising avenue for reducing energy consumption, minimizing environmental impact, and promoting sustainable living practices.
Integration of smart thermostats and energy monitoring devices
The integration of smart thermostats and energy monitoring devices represents a significant step towards energy efficiency and sustainability in smart home ecosystems. Smart thermostats utilize advanced algorithms and sensors to optimize heating and cooling systems based on factors such as occupancy, temperature preferences, and weather conditions.
By integrating with energy monitoring devices, such as smart meters or energy monitors, smart thermostats can provide users with real-time insights into their energy consumption patterns. This allows users to identify areas of inefficiency and make informed decisions about how to reduce energy usage and lower utility bills.
Furthermore, smart thermostats can communicate with other smart home devices, such as smart lighting systems and appliances, to coordinate energy usage and optimize overall energy efficiency. For example, a smart thermostat can adjust temperature settings based on occupancy detected by motion sensors, ensuring that heating and cooling systems are only used when needed.
Impact of smart home technology on energy conservation
The impact of smart home technology on energy conservation is profound, offering opportunities to reduce energy consumption, lower utility bills, and minimize environmental impact. Smart home devices, such as smart thermostats, lighting systems, and appliances, can optimize energy usage through automation, scheduling, and remote control features.
One of the key benefits of smart home technology is its ability to provide users with greater visibility and control over their energy usage. Energy monitoring devices allow users to track their energy consumption in real time, identify energy-intensive appliances or behaviors, and make adjustments to reduce waste.
Furthermore, smart home devices can automate energy-saving measures based on user preferences and environmental conditions. For example, smart thermostats can adjust temperature settings when occupants are away from home or asleep, optimizing energy usage without sacrificing comfort.
Moreover, the integration of renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines into smart home ecosystems further enhances energy conservation efforts. Smart home systems can monitor energy production and consumption, allowing users to maximize the use of renewable energy and minimize reliance on the grid.
Adoption of renewable energy sources within smart home ecosystems
The adoption of renewable energy sources within smart home ecosystems is a key component of sustainable living and energy conservation efforts. Renewable energy sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal systems offer clean and sustainable alternatives to traditional fossil fuels, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and minimize environmental impact.
Smart home technology facilitates the integration and management of renewable energy sources by providing users with real-time insights and control over energy production and consumption. For example, smart energy management systems can monitor solar panel output, battery storage levels, and household energy usage, allowing users to maximize the use of renewable energy and optimize overall energy efficiency.
Furthermore, smart home systems can coordinate energy usage with renewable energy production to minimize reliance on the grid and reduce utility bills. For example, energy storage systems can store excess energy generated by solar panels during the day for use during peak demand periods or when solar production is low.
Moreover, smart home ecosystems can leverage advanced algorithms and predictive analytics to optimize energy usage based on renewable energy availability and weather conditions. For example, smart thermostats can adjust temperature settings based on solar production forecasts, ensuring that heating and cooling systems are used when renewable energy is plentiful.
Expansion Beyond the Household
The influence of smart home technology extends far beyond individual households, encompassing broader applications in urban planning, infrastructure development, and community management. As cities grapple with challenges such as population growth, urbanization, and environmental sustainability, smart home technology offers innovative solutions to enhance efficiency, connectivity, and quality of life on a larger scale.
Integration of smart home technology in urban planning and infrastructure
The integration of smart home technology in urban planning and infrastructure represents a significant advancement in creating smarter, more efficient cities. By incorporating interconnected devices, sensors, and data analytics into urban infrastructure, city planners can optimize resource usage, improve service delivery, and enhance the overall quality of life for residents.
Smart home technology plays a crucial role in various aspects of urban planning and infrastructure development. For example, smart building systems can monitor energy usage, occupancy levels, and indoor air quality to ensure efficient operation and occupant comfort. Additionally, smart transportation systems use real-time data from sensors and traffic cameras to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and enhance road safety.
Moreover, smart home technology enables the development of intelligent utility infrastructure, such as smart grids and water management systems. These systems use sensors and data analytics to monitor energy and water usage, detect leaks or anomalies, and optimize distribution to minimize waste and improve efficiency.
Smart city initiatives and their reliance on interconnected devices
Smart city initiatives rely heavily on interconnected devices and sensors to collect, analyze, and act on data in real time. These initiatives leverage the Internet of Things (IoT) to create interconnected networks of devices, infrastructure, and services that enable cities to operate more efficiently and effectively.
One example of a smart city initiative is the implementation of smart lighting systems. These systems use sensors and connected LED lights to adjust brightness levels based on ambient light conditions, occupancy patterns, and traffic flow. This not only reduces energy consumption and light pollution but also improves public safety and security.
Another example is the deployment of smart waste management systems, which use sensors to monitor waste levels in bins and optimize collection routes to reduce costs and minimize environmental impact. By leveraging interconnected devices and data analytics, cities can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of essential services while enhancing sustainability and livability for residents.
Implications for future urban development and sustainability efforts
The integration of smart home technology in urban planning and infrastructure has far-reaching implications for future urban development and sustainability efforts. By creating more connected, intelligent, and resilient cities, smart home technology can help address pressing challenges such as population growth, urbanization, and climate change.
One key implication is the potential for more sustainable and resource-efficient cities. By optimizing resource usage, reducing waste, and promoting renewable energy sources, smart cities can minimize their environmental footprint and enhance resilience to climate change impacts such as extreme weather events and rising sea levels.
Moreover, smart home technology enables more efficient and equitable service delivery, improving access to essential services such as healthcare, education, and transportation for all residents. By leveraging data-driven insights and collaborative platforms, cities can address social and economic disparities and promote inclusive urban development.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of smart home technology promises to be filled with exciting trends and innovations that will continue to transform the way we live, work, and interact with our homes. As technology advances and consumer preferences evolve, several key trends and innovations are expected to shape the future of smart home technology.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning technologies will play an increasingly significant role in smart home devices, enabling them to become more intelligent, intuitive, and personalized. AI-powered assistants will become even more sophisticated, anticipating users’ needs, learning from their behaviors, and providing proactive recommendations and assistance.
Enhanced Connectivity and Interoperability
Future smart home devices will feature enhanced connectivity and interoperability, allowing them to seamlessly communicate and integrate. Standardized communication protocols and interoperability standards will enable greater compatibility between devices from different manufacturers, creating cohesive and interconnected smart home ecosystems.
Edge Computing and Distributed Intelligence
Edge computing technologies will become more prevalent in smart home devices, enabling them to process data locally and make real-time decisions without relying on cloud-based servers. This distributed intelligence will improve responsiveness, reduce latency, and enhance privacy and security by keeping sensitive data closer to home.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Sustainable and energy-efficient solutions will continue to be a major focus in smart home technology, with an emphasis on reducing energy consumption, minimizing environmental impact, and promoting eco-friendly practices. Smart home devices will feature energy-saving features, renewable energy integration, and resource-efficient design to support sustainability efforts.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR technologies will revolutionize the way we interact with smart home devices and visualize our living spaces. AR-enabled smart home apps will allow users to virtually place and visualize furniture, appliances, and home decor before making purchase decisions. VR simulations will enable users to experience and interact with their homes in immersive virtual environments.
Read More: Exploring the Future of Virtual Reality Gaming
Health and Wellness Monitoring
Smart home devices will increasingly focus on health and wellness monitoring, helping users track and manage their physical and mental well-being. From smart mattresses and sleep trackers to connected fitness equipment and biometric sensors, future smart home devices will provide insights and recommendations to support healthy lifestyles.
Enhanced Security and Privacy Features
As smart home technology becomes more ubiquitous, security and privacy features will become increasingly important. Future smart home devices will feature advanced encryption, biometric authentication, and privacy-enhancing technologies to protect user data and safeguard against cyber threats.
Personalization and Customization
Personalization and customization will be key trends in future smart home technology, with devices and systems adapting to individual user preferences and lifestyles. AI algorithms will analyze user data and behaviors to tailor experiences, automate routines, and provide personalized recommendations and suggestions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the evolution of smart home technology has transformed the way we interact with our living spaces, offering unprecedented convenience, efficiency, and connectivity. From the early beginnings of simple automation to the integration of artificial intelligence and sustainable solutions, smart home technology has continuously evolved to meet the changing needs and preferences of users.